What Is HR Compliance?
HR compliance ensures that a company adheres to the laws and regulations governing labor practices. This means setting up policies and procedures that align with federal, state, and local laws to create a fair and legal workplace.
Compliance covers everything from hiring practices and wage laws to safety regulations and anti-discrimination policies. For example, businesses must follow the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), which regulates minimum wage, overtime pay, and recordkeeping requirements.
Maintaining HR compliance protects the organization from legal penalties and helps build a positive reputation as a fair and ethical employer. It requires constant attention and updating to stay current with the ever-changing laws and regulations that apply to different aspects of the workplace.
There are several types of compliance within HR. Let’s explore four key areas:
-
Statutory Compliance: This involves adhering to government legislation related to employment and the workplace. For example, your company must follow laws regarding minimum wage, working age requirements, and anti-discrimination practices.
-
Regulatory Compliance: While similar to statutory compliance, regulatory compliance focuses on adhering to the rules of specific regulatory bodies. These agencies can be classified into three categories: independent regulatory commissions like the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), executive agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and government corporations like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
-
Contractual Compliance: This type of compliance involves following the regulations and terms outlined in contracts your organization is bound by. These can be agreements between your company and partner organizations or contracts with your employees.
-
Union Law Compliance: For companies employing union workers, it’s essential to comply with the rules set by these unions. For instance, the Screen Actors Guild represents over 100,000 performers and technicians, and your company must adhere to the guidelines established by such unions.
Why HR Compliance Is Important
Ensuring HR compliance is not just about avoiding legal trouble; it’s about building a foundation for a thriving and sustainable business. Here are the key reasons why HR compliance is crucial for your organization:
1. Legal Protection
HR compliance is essential for legal protection. Adhering to labor laws and regulations shields businesses from lawsuits, fines, and other legal repercussions. For instance, failing to comply with wage and hour laws can result in costly penalties and back pay Ensuring compliance helps mitigate these risks, safeguarding the company’s financial health.
2. Reputation Management
A company’s reputation hinges on how it treats its employees and adheres to legal standards. Companies known for their compliance are seen as ethical and trustworthy, which can enhance their reputation in the market. This positive image can attract top talent and foster customer loyalty.
3. Employee Satisfaction
Compliance with labor lawsensures fair treatment of employees, which directly impacts their satisfaction and morale. When employees know their rights are protected, they feel valued and secure. This sense of security leads to higher productivity, loyalty, and retention rates.
4. Create a Positive Work Environment
A compliant workplace is a positive one, where employees feel safe and respected. Adhering to health and safety regulations, anti-discrimination laws, and fair labor practices creates an environment where employees can thrive. This not only boosts morale but also enhances overall organizational performance.
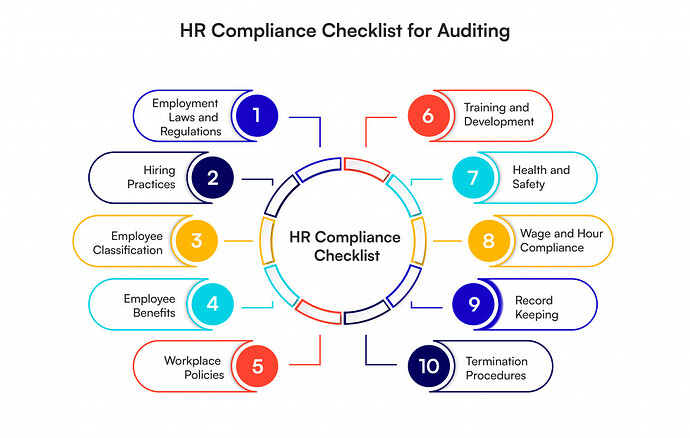
HR Compliance Checklist
A comprehensive HR compliance checklist ensures that all aspects of the business align with relevant laws and regulations. Here are the key areas to focus on:
1. Employment Laws and Regulations
Adherence to federal, state, and local labor laws is fundamental for HR compliance. Key laws include:
-
Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA): Regulates minimum wage, overtime pay, and child labor.
-
Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA): Provides eligible employees with unpaid, job-protected leave for certain family and medical reasons.
-
Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA): Ensures workplace safety and health standards.
-
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act: Prohibits employment discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.
-
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA): Prohibits discrimination based on disability and requires reasonable accommodations.
2. Hiring Practices
Implementing non-discriminatory hiring practices is crucial. Ensure job listings and interview questions do not reveal or imply biases based on protected characteristics. Comply with laws such as:
-
Equal [Employment Opportunity Act (EEOA): Prohibits discrimination against job applicants based on race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age, disability, or genetic information.
-
Ban the Box Laws: Restrict employers from asking about criminal history on job applications before a certain stage of the hiring process .
3. Employee Classification
Properly classify employees as exempt or non-exempt under the FLSA to ensure compliance with wage and hour laws. Misclassification can lead to significant legal and financial consequences:
-
Exempt Employees: Not entitled to overtime pay; typically salaried employees meeting certain criteria.
-
Non-Exempt Employees: Entitled to overtime pay; often hourly workers or those not meeting exemption criteria .
4. Wage and Hour Compliance
Ensure compliance with minimum wage laws, overtime pay, and accurate timekeeping. Regular audits of payroll processes help prevent errors:
-
Minimum Wage: Comply with federal, state, and local minimum wage laws, which may vary.
-
Overtime Pay: Ensure non-exempt employees receive overtime pay for hours worked beyond the standard 40-hour workweek.
-
Recordkeeping: Maintain accurate records of hours worked and wages paid .
5. Employee Benefits
Providing mandatory benefits and ensuring they comply with federal and state laws is essential:
-
Affordable Care Act (ACA): Requires employers with 50 or more full-time employees to offer minimum essential health care coverage.
-
Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA): Sets minimum standards for retirement and health benefit plans.
-
Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA): Mandates unpaid, job-protected leave for eligible employees .
6. Workplace Policies
Develop and enforce comprehensive workplace policies that comply with relevant laws and regulations. These policies should cover a wide range of issues to ensure a fair and safe working environment. Key areas to address include:
-
Anti-Discrimination and Harassment: Implement policies that prohibit discrimination and harassment based on race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age, disability, or genetic information. Clearly define unacceptable behaviors and outline procedures for reporting and handling complaints.
-
Dress Codes and Appearance: Establish guidelines for appropriate workplace attire and personal appearance. These policies should be reasonable and non-discriminatory, respecting cultural and religious practices.
-
Work Hours and Breaks: Set clear expectations for work hours, breaks, and meal periods. Ensure compliance with federal and state laws regarding overtime pay and mandatory breaks. For example, the FLSA requires that employees be paid for breaks lasting 20 minutes or less.
-
Remote Work Policies: With the rise of remote work, establish policies that address expectations for remote employees, including communication protocols, work hours, and data security.
7. Training and Development
Regular training is crucial for ensuring compliance and maintaining a knowledgeable workforce. Key areas for training include:
-
Compliance Training: Provide training on relevant laws and regulations, including anti-discrimination, harassment prevention, and safety protocols. In California, employers with five or more employees must provide anti-harassment training to all employees.
-
Safety Training: Conduct regular safety training sessions to ensure employees understand workplace hazards and safety procedures. This helps prevent accidents and ensures compliance with OSHA regulations.
-
Policy Training: Educate employees about company policies and procedures, including code of conduct, disciplinary actions, and reporting mechanisms. This helps ensure that employees understand their rights and responsibilities.
-
Skills Development: Offer ongoing professional development opportunities to help employees enhance their skills and stay updated with industry best practices. This not only boosts compliance but also improves overall job performance.
8. Health and Safety
Maintaining a safe working environment is a top priority for compliance and employee well-being. Steps to ensure health and safety include:
-
OSHA Compliance: Adhere to OSHA standards by conducting regular safety audits, implementing safety protocols, and providing necessary protective equipment. Employers must also maintain accurate records of workplace injuries and illnesses.
-
Emergency Preparedness: Develop and communicate emergency response plans for various scenarios, such as fires, natural disasters, and workplace violence. Conduct regular drills to ensure employees are prepared for emergencies.
-
Health Programs: Implement health and wellness programs to promote employee well-being. This can include offering health screenings, mental health support, and ergonomic assessments to prevent workplace injuries.
-
COVID-19 Compliance: Ensure adherence to guidelines for COVID-19 prevention, including social distancing, sanitation, and health monitoring. This helps protect employees and prevent outbreaks in the workplace.
9. Record Keeping
Accurate and secure record keeping is essential for compliance and legal protection. Key practices include:
-
Employment Records: Maintain detailed records of employee information, including job applications, performance reviews, disciplinary actions, and termination documents. Ensure these records are kept confidential and stored securely.
-
Payroll Records: Keep accurate records of wages, hours worked, overtime, and deductions. This is crucial for complying with wage and hour laws and resolving any payroll disputes.
-
Benefits Records: Document employee benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and leave entitlements. Ensure records are up-to-date and comply with regulations such as the ACA and ERISA.
-
Compliance Documentation: Maintain records of compliance activities, such as safety audits, training sessions, and policy updates. Proper documentation is essential for audits and demonstrating compliance to regulatory agencies.
10. Termination Procedures
Following legal guidelines for employee termination helps avoid wrongful termination lawsuits and ensures a smooth transition for departing employees. Key steps include:
-
Notice Periods: Provide the required notice period as specified by law or employment contracts. This gives employees time to prepare for their departure and helps maintain goodwill.
-
Severance Pay: Offer severance pay if applicable, based on company policy or legal requirements. Clearly communicate the terms of severance to the departing employee.
-
Final Paychecks: Ensure that final paychecks are processed accurately and on time. This includes payment for any unused vacation days, bonuses, and other owed compensation.
-
Exit Interviews: Conduct exit interviews to gather feedback from departing employees. This can provide valuable insights for improving workplace practices and addressing any underlying issues.
-
Documentation: Document the termination process thoroughly, including the reasons for termination and any communications with the employee. Proper documentation helps protect the company in case of legal disputes.